Water Use Efficiency Component
Under this component, there are three projects related to efficient water use. Two of these - Demonstration of Multi-functionality on Paddy Fields (DMPF) and Improvement of Irrigation Efficiency on Paddy Fields (IIEPF) -, are funded by the Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. The third one, the Challenge Program on Water and Food is supported by The Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR).
Demonstration of Multi-functionality
on Paddy Fields
The DMPF project, which started from 2002, primarily aimed
to analyze various functions of paddy fields and their contributions
to basin wide scale.
Apart from food production, paddy fields and paddy irrigation water have various functions including flood mitigation, ground water recharge, stabilizing river flow and re-use of irrigation water, soil erosion control, land slide prevention, water purification, microclimate mitigation, protection of biodiversity, nurturing of aquatic ecosystems and aquaculture, organic waste processing and multiple domestic uses.
The first stage of the project (which culminated in the third regional workshop held in Hai Phong, Viet Nam in August 2005) mainly focused on related data collection at both basin wide and experimental fields level. Through this process, the DMPF project created several interesting graphical data, such as a land use map, which differentiates paddy fields from other agricultural land use (pdf), a monthly rice planted area map(pdf), a comparison map of planted area and rainfall(pdf), an animation of rice planted area and rainfall (ppt 42MB*). The DMPF project also reviewed and updated an irrigation scheme database. (Summary is linked here in pdf.)
The DMPF project has also estimated irrigation water use, based on various available data. This work was conducted in three stages in 2005 and the final report is available here (pdf), and the annex is also available here (pdf 10MB*). The map of monthly irrigation wateave cr use by scheme is also available here (pdf).
Following a review of the achievements and constraints of the first stage, the second stage of the DMPF project has slightly modified the project direction and is concentrating on providing a clear or better understanding of paddy fields' multi-functionality through showing visible examples of some selected functions in some selected areas with quantified evaluation. Two teams of regional consultants have carried out this analysis work. A Thai team in North East Thailand examined three functions: flood mitigation, nurturing of aquatic ecosystems and maintenance of agro-ecosystem biodiversity, and buffering farmers against environmental risks. The Vietnamese team studied four functions in the Mekong Delta: flood mitigation, soil conservation, nurturing aqua-ecosystems and socio-economic functions. The results of this analysis work were presented at the wrap-up workshop held at MRC Secretariat, Vientiane in August 2007. The workshop proceedings are available here(pdf 10.5MB*). This project will close its activities by completion of the final report by the end of 2007.
Improvement of Irrigation Efficiency
on Paddy Fields
Since rice is the single biggest consumptive user of fresh
water in the region, effective water use on paddy field irrigation
is vital for both further agricultural development and development
in other water related sectors. A new, three-year project
aiming to improve irrigation efficiency through providing
guidance to water managers was launched in July 2005. The
first regional workshop was held in May 2006 to inaugurate
the project.
The project aims "to improve irrigation efficiency on paddy fields in the Lower Mekong Basin" as its overall objective and has set three immediate objectives to realise this:
- to appraise irrigation efficiencies and the irrigation system based on modern concepts in the selected irrigation schemes;
- to enhance capacity of all the stakeholders in using up-to-date concepts of irrigation efficiencies and water balance and modern tools and procedures for their assessment; and
- to produce guidelines for improving irrigation efficiency on paddy field based on actual water use conditions in the member countries.
In order to achieve these three objectives, the project is now conducting to analysis of actual irrigation efficiencies based on intensive field observation at selected schemes, to assess the performance of those schemes in terms of technical, managerial and institutional aspects, and then to produce the guidelines based on those findings from the field.
For efficiencies' analysis, a modern concept of water balance, which takes into account interaction between surface and ground water, is being applied. For scheme performance assessment, the Rapid Appraisal Process (RAP) jointly developed by FAO and the World Bank has been applied as a diagnosis tool.
As the project progresses it has presented its achievements on various occasions. The Basic concept was introduced at an international conference in Chiang Rai, Thailand in October 2006, and a paper on Assessed irrigation efficiency and water productivity based on 2006/07 dry season observation was presented at the 3rd South East Asia Water Forum held in Kuala Lumpur in October 2007.
For more details of this project please access the project document(pdf), project brochure(pdf) and the first regional workshop proceedings(zip), RAP Training Workshop and initial Assessment report, which are now available on this site. Other publications (1, 2, 3, 4) will be posted on this site according to the progress.
* File size is only indicated where files are 5MB or larger.
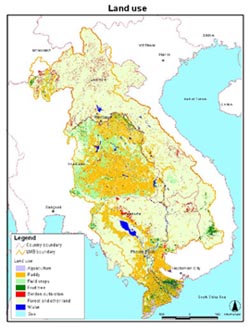
Land use map. Click on the map to enlarge
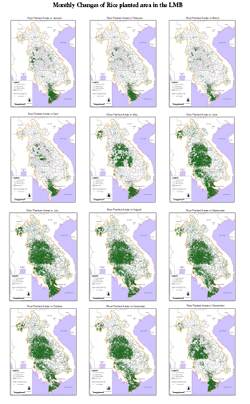
Monthly Changes of Rice planted area
in the LMB. Click on the image to view details (in pdf)
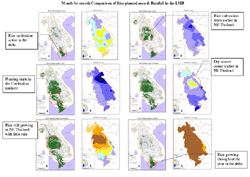
Month-by-month Comparison of Rice planted
area & Rainfall in the LMB. Click on the image to view
details (in pdf)
Click here for animation (ppt 42MB)
Choose a newsletter:
 Top
Top