River Basin Management
River basin – a natural unit
Water does not stop at administrative or political boundaries, so the best way to protect and manage water is by close international co-operation between all the countries within the natural geographical and hydrological unit of the river basin – bringing together all interests upstream and downstream.
What are river basin districts?
Areas of land and sea identified as the main managment unit are known as river basin districts. These regions can include one or more neighbouring river basins together with their associated groundwater bodies and coastal waters. The Danube River Basin District covers the Danube River Basin, the Romanian Black Sea coastal catchments and the Black Sea coastal waters along the Romanian and partly the Ukrainian coast.
All European waters are managed using a river basin approach since 2000 when the EU Water Framework Directive was adopted by the European Union – creating a new tool for the effective management of water resources.
Managing the Danube River Basin
To achieve good water status in the water bodies of the Danube region by 2015 (and beyond) and to ensure a sufficient supply of clean water for future generations, the Contracting Parties to the DRPC nominated the ICPDR as the co-ordination body for the development of a comprehensive management plan for the entire Danube River Basin using the principles of the EU Water Framework Directive. This process involves experts from industry and agriculture, and representatives from environmental and consumer organisations as well as the local and national authorities. The Danube River Basin Management Plan is to be updated every six years according to EU legislation.
The DRBM Plan focuses on the main transboundary problems, so called Significant Water Management Issues (SWMI), that can directly or indirectly affect the quality of rivers and lakes as well as transboundary groundwater bodies:
• Pollution by organic substances
• Pollution by nutrients
• Pollution by hazardous substances
• Hydromorphological alterations
The Plan includes visions and objectives for each SWMI as well as a Joint Programme of Measures. In addition, the Plan includes:
- a description of the significant pressures in the DRB
- an overview on the monitoring networks
- an assessment of the ecological and chemical status
- a final designation of Heavily Modified Water Bodies
- an overview on exemption according to the EU WFD
- an economic analysis of water uses
- a brief overview on water quantity issues and climate changes
- an outline of public consultation and participation
- an inventory of protected areas
The final version of the DRBM Plan is available since end of 2009 and has been adopted at the ICPDR Ministerial Meeting in February 2010.
Ambitious deadlines
The ICPDR follows the ambitious deadlines set out in the EU Water Framework Directive.
| 2004 | Characterisation of river basin: pressures, impacts and economic analysis (Art. 5) |
| 2006 | Establishment of monitoring network (Art. 8) |
| 2008 | Presentation of draft river basin management plan (Art. 13) |
| 2009 | Finalisation of river basin management plan, including programmes of measures (Art. 13 and 11) |
| 2010 | Introduction of pricing policies (Art. 9) |
| 2012 | Operationalisation of programmes of measures (Art. 11) |
| 2015 | Meet environmental objectives (Art. 4) |
| 2015-2021 | 2nd management cycle |
| 2021-2027 | 3rd management cycle |
The Water Framework Directive
To meet the challenge of ensuring a sufficient supply of clean water for future generations the European Community adopted in December 2000 the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD) - a new and effective tool for water management.
Did you know?
The state of European water resources is relatively favourable compared to other regions of the world. There is generally enough water, but in many areas its quality is inadequate
The WFD establishes a legal framework to protect and enhance the status of aquatic ecosystems; prevent their deterioration and ensure long-term, sustainable use of water resources. The Directive provides for an innovative approach for water management based on river basins, the natural geographical and hydrological units, and sets specific deadlines for EU Member States. The WFD addresses inland surface waters (rivers and lakes), transitional waters, coastal waters, groundwater and, under specific conditions, water dependent terrestrial ecosystems and wetlands. It establishes several integrative principles for water management, including public participation in planning and the integration of economic approaches, and also aims for the integration of water management into other policy areas. For better coordination, the WFD calls for the creation of international districts for river basins that cover the territory of more than one EU Member State. EU Member States should aim to achieve good status in all bodies of surface water and groundwater by 2015, respectively by 2027 at the latest.
Information and Consultation of the Public
Involvement of the public and proactive information sharing are key principles for river basin management. Therefore, the ICPDR publishes all basin-wide startegic documents and analysis reports.
The latest strategic document is the interim overview on the Significant Water Managment Issues in the Danube River Baisn District, which is the basis for the Danube River Basin Management Plan.
In case you can not find the specific document you are looking for, please do not hesitate contacting us!
For more information
Guidance document No. 11. Planning Processes (see Related Links). A CD-ROM “Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive") is available from the Publications Office of the European Communities.
Significant Water Management Issues in the DRB District
Significant Water Management Issues in the Danube River Basin District (including visions and management objectives for each significant water management issue)
Background on hazardous substances in the Danube river basin for the "Significant Water Managment Issues Paper"
Background on hydromorphological alterations in the Danube river basin for the "Significant Water Managment Issues Paper"
Background on nutrient pollution in the Danube river basin for the "Significant Water Managment Issues Paper"
Background on organic pollution in the Danube river basin for the "Significant Water Managment Issues Paper"
Strategic Paper for the Development of a Danube River Basin District Management Plan - Draft 9
Danube Basin Analysis (WFD Roof report 2004)
The Danube River Basin District - River basin characteristics, impacts of human activities and economic analysis required under Article 5, Annex II and Annex III, and inventory of protected areas required under Article 6, Annex IV of the EU Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC) - Part A -...
Fulltext (PDF, 5MB)
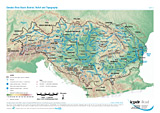
Danube River Basin District Overview
Layer: Competent authority
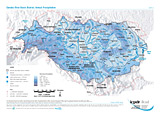
Annual Precipitation
Layer: Total Annual Precipitation
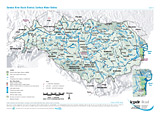
Surface Water Bodies
Layers: River water bodies, Lake water bodies (surface area > 100 km²), Transitional waters bodies, Coastal water bodies, Artificial water bodies
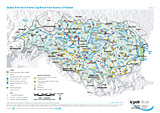
Significant Point Sources of Pollution
Layers: Nuclear power plants, Significant Point Sources (Municipal WWTP, Municipal untreated, Industrial, Agicultural)
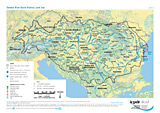
Land Use
Layer: Aggregated land use classes (Coniferous forest, Deciduous forest, Grassland, Wetlands, Arable land, Urbanized area, Sparsly vegetated area, Sea)

Major Hydraulic Structures
Layers: Hydraulic structures (mainly dams and weirs), Harbours, Waterways ECE I-IV, Waterways ECE V-VII, Free flowing river stretch, Strongly regulated river stretch, Impounded river stretch

Potential Accident Risk Spots
Layers: Potential Accident Risk Spots (WRI 5-6, WRI 6-7, WRI 7-8, WRI 8-9)

Old Contaminated Sites in Potentially Flooded Areas
Layer: Old contaminated sites

Important Heavily Modified Surface Waters (provisional identification)
Layers: Transitional waters, Coastal waters, Heavily modified surface waters (aggregated water bodies according to aggreed criteria for basin-wide importance)
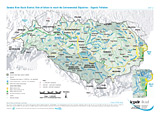
Risk of failure to reach the Environmental Objectives - Organic Pollution
Layers: Surface Water Bodies (Water body at risk, Water body possibly at risk, Water body not at risk)
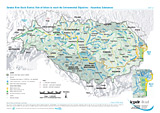
Risk of failure to reach the Environmental Objectives - Hazardous Substances
Layers: Surface Water Bodies (Water body at risk, Water body possibly at risk, Water body not at risk)

Risk of failure to reach the Environmental Objectives - Nutrient Pollution
Layers: Surface Water Bodies (Water body at risk, Water body possibly at risk, Water body not at risk)

Risk of failure to reach the Environmental Objectives - Hydromorphological Alterations
Layers: Surface Water Bodies (Water body at risk, Water body possibly at risk, Water body not at risk)

Important Transboundary Groundwater Bodies
Layers: Important transboundary groundwater bodies of different horizons (transboundary areas > 4000 km²)
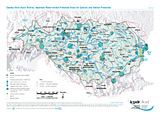
Important Water-related Protected Areas for Species and Habitat Protection
Layers: Areas for species and habitat protection (< 10,000 ha, 10,000 - 50,000 ha, > 50,000 ha), Transboundary co-operation
Disclaimer
The information contained in the ICPDR website is intended to enhance public access to information about the ICPDR and the Danube River. The information is correct to the best of the knowledge of the ICPDR Secretariat. If errors are brought to our attention we will try to correct them.
The ICPDR, expert group members, nor other parties involved in preparation of information contained on this website cannot, however, be held responsible for the correctness and validity of the data and information provided, nor accept responsibility or liability for damages or losses arising directly or indirectly from the use of the information conveyed therein.
Only those documents clearly marked ICPDR documents reflect the position of the ICPDR.
Any links to other websites are provided for your convenience only. The ICPDR does not accept any responsibility for the accuracy, availability, or appropriateness to the user's purposes, of any information or services on any other website.
When using the information and material provided on this website, credit should be given to the ICPDR.

